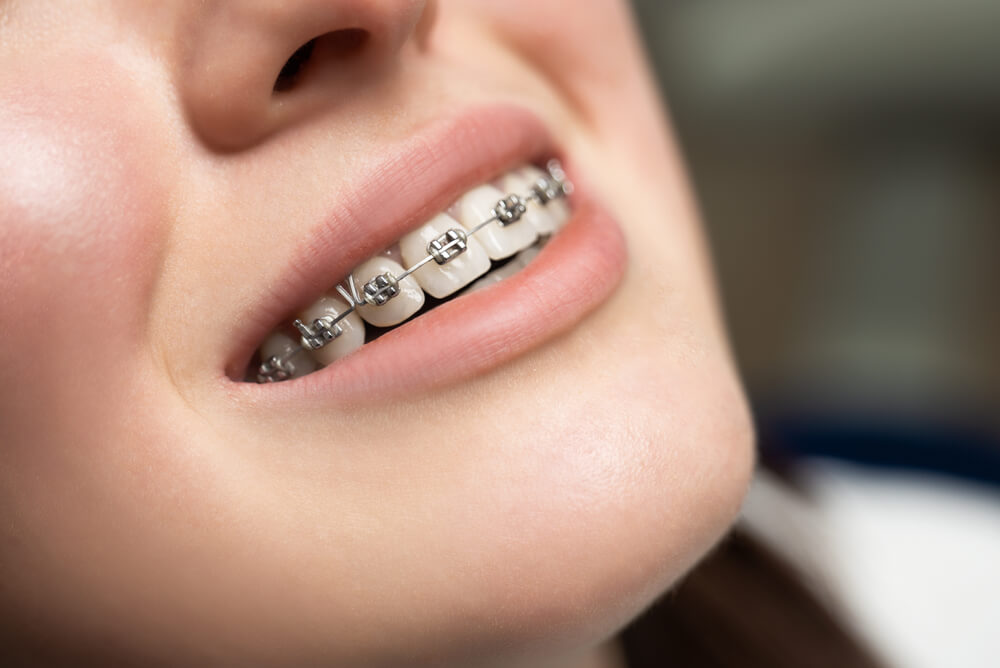
How do braces work?
Braces are a type of dental appliance that are used to straighten and align teeth. They work by applying continuous, gentle pressure to the teeth, which over time moves them into the desired position. Braces typically consist of metal brackets that are bonded to the teeth and connected by a wire. The wire is held in place by small elastic bands called ligatures, which help to keep the wire and brackets together.
The process of straightening teeth with braces begins with a consultation and examination by an orthodontist, who will determine the best course of treatment for each individual patient. Once the braces are in place, the patient will need to regularly visit the orthodontist to have the wire tightened, which increases the pressure on the teeth and moves them into the desired position. The length of treatment with braces can vary, but most patients wear them for 18 to 24 months.
In addition to traditional metal braces, there are also other types of braces, including clear plastic aligners, ceramic braces, and lingual braces, which are attached to the back of the teeth instead of the front. The specific type of braces used will depend on the patient's individual needs and preferences.